
Lumens to Watts Conversion: A Complete Guide to Efficient Lighting Choices
Share
Table of Contents
- What are lumens?
- What are watts?
- Lumens to Watts Conversion Chart
- How Many Lumens in a Watt?
- Factors Affecting LED Efficiency
- Practical Examples and Personal Experiences
- Conclusion: Why Focus on Lumens
- FAQs

1. What are lumens?
Lumens (lm) are the measurement of the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. In simple terms, lumens measure the brightness of the bulb. When selecting lighting, you need to focus on lumens to ensure that the bulb provides enough light for your intended use.
Why Lumens Matter:
Lumens tell you how bright a bulb will be, regardless of the energy it consumes. For example, a 60-watt incandescent bulb typically produces around 800 lumens, whereas a 10-watt LED bulb can produce the same amount of light while consuming far less energy.
2. What are watts?
Watts (W) measure the power consumption of a bulb. Traditionally, watts were used as a proxy for brightness, but with energy-efficient LEDs, this no longer holds true. Watts now primarily tell you how much energy a bulb uses, but they don’t necessarily correlate with brightness, especially in the case of LEDs.
Why Watts Matter Less with LEDs:
LED technology has revolutionized energy efficiency. For instance, a 10-watt LED bulb can provide the same brightness as a 60-watt incandescent bulb, making LEDs much more energy-efficient.
3. Lumens to Watts Conversion Chart: Your Quick Reference Guide
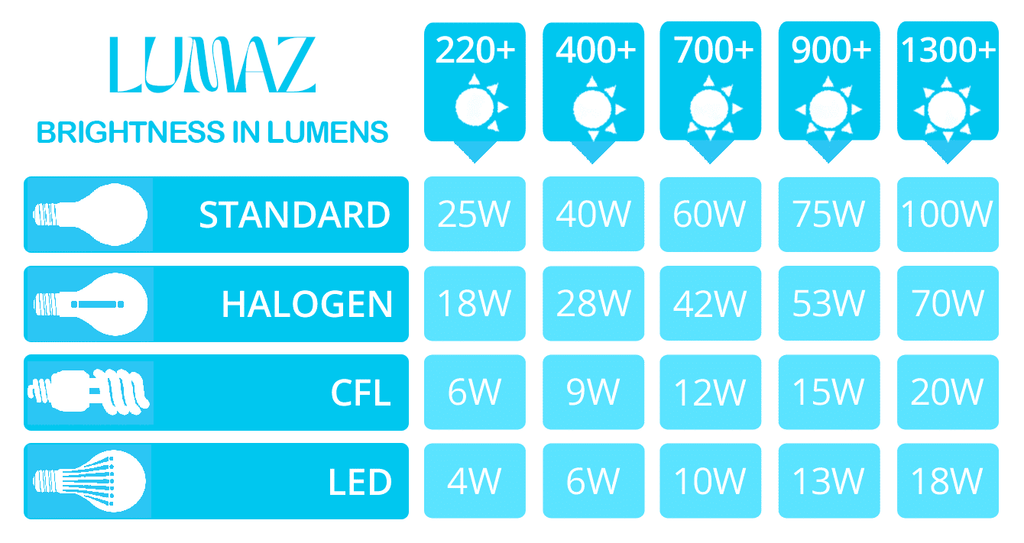
To help you better understand the relationship between lumens and watts, here’s a lumens to watts conversion chart that shows the equivalencies for different types of bulbs:
Note: The figures in the chart below are all approximate wattage
| Lumens | LED Watts | Incandescent Watts | Halogen Watts |
| 100 | 1-2 | 15 | 10 |
| 300 | 4-6 | 30 | 25 |
| 500 | 8-12 | 50 | 45 |
| 800 | 13-20 | 75 | 75 |
| 1000 | 16-25 | 90 | 95 |
| 1200 | 18-30 | 100 | 115 |
| 1600 | 22-40 | 130 | 155 |
| 1800 | 25-45 | 145 | 175 |
| 2000 | 27-50 | 160 | 195 |
| 5000 | 65-125 | 400 | 495 |
| 10000 | 130-250 | 800 | 990 |
This chart demonstrates that LED bulbs consume significantly less energy while providing the same brightness as traditional bulbs.
LED Lumens to Watts Conversion Tool
4. How Many Lumens in a Watt?
The efficiency of light bulbs varies depending on the type. For example:
- LED Bulbs: Lumens = Watts x 80 (approx.)
- CFL Bulbs: Lumens = Watts x 70 (approx.)
- Halogen Bulbs: Lumens = Watts x 20 (approx.)
- Incandescent Bulbs: Lumens = Watts x 15 (approx.)
Let’s take a 100-watt LED bulb. Using the formula above:
- 100 watts x 80 = 8,000 lumens.
This demonstrates the immense efficiency of LED bulbs when compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, which produce only about 1,500 lumens for the same wattage.
5. Factors Affecting LED Efficiency
- LED Quality: Higher-quality LEDs can produce more lumens per watt. Premium LEDs from brands like Cree and Philips are often more efficient than cheaper options.
- Heat Dissipation: Good heat regulation helps LEDs maintain their brightness over time.
- Color Temperature: Light bulbs with cooler color temperatures (e.g., 4000K-5000K) may appear brighter than warmer bulbs (2700K-3000K) at the same lumen output.
- Voltage Regulation: High-quality LED drivers help ensure the light bulb maintains efficiency without overheating.
6. Practical Examples and Personal Experiences
Home Lighting Upgrade:
I replaced 60W incandescent bulbs in my living room with 8W LED bulbs, each providing 800 lumens. The energy savings were significant, reducing my electricity bill by about 80%. Plus, the LEDs' longer lifespan meant fewer replacements.
Office Lighting:
In an office project, we used 1600-lumen (16W) LED bulbs to replace 100W incandescent bulbs. The improved lighting reduced eye strain and boosted productivity, while also cutting energy costs.
Outdoor Lighting:
For a friend's garden, we replaced 40W incandescent bulbs with 450-lumen (5W) LEDs. These provided ample lighting for pathways and reduced energy use, proving durable in outdoor conditions.
Further Reading:
- What is the best lumens for under cabinet lighting?
- How to Choose the Right Wattage for Under Cabinet Lighting
- What is the best lumens for LED Puck Lights?
7. Conclusion: Why Focus on Lumens
When choosing light bulbs, lumens should be your primary concern, as they directly correlate with the brightness you need. While watts are important for understanding energy usage, focusing on lumens ensures that you get the right amount of light while saving energy. By switching to LED bulbs, you can reduce both your energy consumption and carbon footprint, making your lighting choices both brighter and more environmentally friendly. This shift to lumens to watts not only helps you save on electricity bills but also contributes to a greener, more sustainable future.
Explore our range of energy-efficient under cabinet lighting solutions at Lumaz to find the perfect fit for your kitchen.
8. FAQs
What is the equivalent wattage of a 100-watt LED bulb compared to an incandescent bulb?
A 100-watt incandescent bulb typically produces about 1600 lumens. A similar brightness level from an LED bulb would only require about 15 to 18 watts. Therefore, a 100-watt incandescent bulb is roughly equivalent to a 15–18-watt LED bulb in terms of light output, providing substantial energy savings.
How do I choose the right lumen output for lighting my room?
The required lumen output varies depending on the purpose of the room. For example, bedrooms and living rooms typically need between 2000 to 3000 lumens, while task-oriented areas such as kitchens and home offices may require higher brightness levels, ranging from 3000 to 5000 lumens.
Is 10,000 lumens too bright?
10,000 lumens is extremely bright and generally too intense for residential use. Such brightness is often used in commercial or industrial settings, like warehouses or large outdoor areas. Proper fixture design and placement are crucial to avoid glare and ensure even light distribution.
How many lumens is extremely bright?
Lumens above 5000 are considered extremely bright. This level of brightness is suitable for large spaces or high-precision tasks. Extremely bright lights are typically used in settings such as sports arenas or large commercial spaces.
What is the highest legal lumens?
The highest legal lumens depend on the application and local regulations. For vehicle headlights in the US, the maximum is around 3000 lumens per headlight. For residential and commercial lighting, there isn't a universal cap, but fixtures must comply with safety standards and local codes.
How many lumens is a police spotlight?
A police spotlight typically ranges from 1000 to 6000 lumens. These spotlights are designed for high visibility and can illuminate distant objects or areas effectively. They are essential for night-time operations and search and rescue missions.
What is the "lumens per watt" rating, and why is it important?
The lumens per watt (lm/W) rating measures the efficiency of a light bulb. It tells you how much light (in lumens) is produced for each watt of energy consumed. A higher lumens per watt rating means a more energy-efficient light bulb, which is crucial for saving energy and reducing electricity costs.
Further Reading:




























 />
/>
 />
/>
 />
/>
 />
/>
 />
/>